如何启用AOP
引入依赖后,类路径存在 Aspect.class、Advice.class、AnnotatedElement.class 因此自动化配置类AopAutoConfiguration生效。
1 | <dependency> |
1 |
|
完整的切面定义
1 |
|
暴露代理类到ThreadLocal
可以通过配置 exposeProxy = true来暴露代理对象到ThreadLocal中,之后在被代理类对象内部可以使用 AopContext.currentProxy() 来获取代理类对象
1 | // 默认为false |
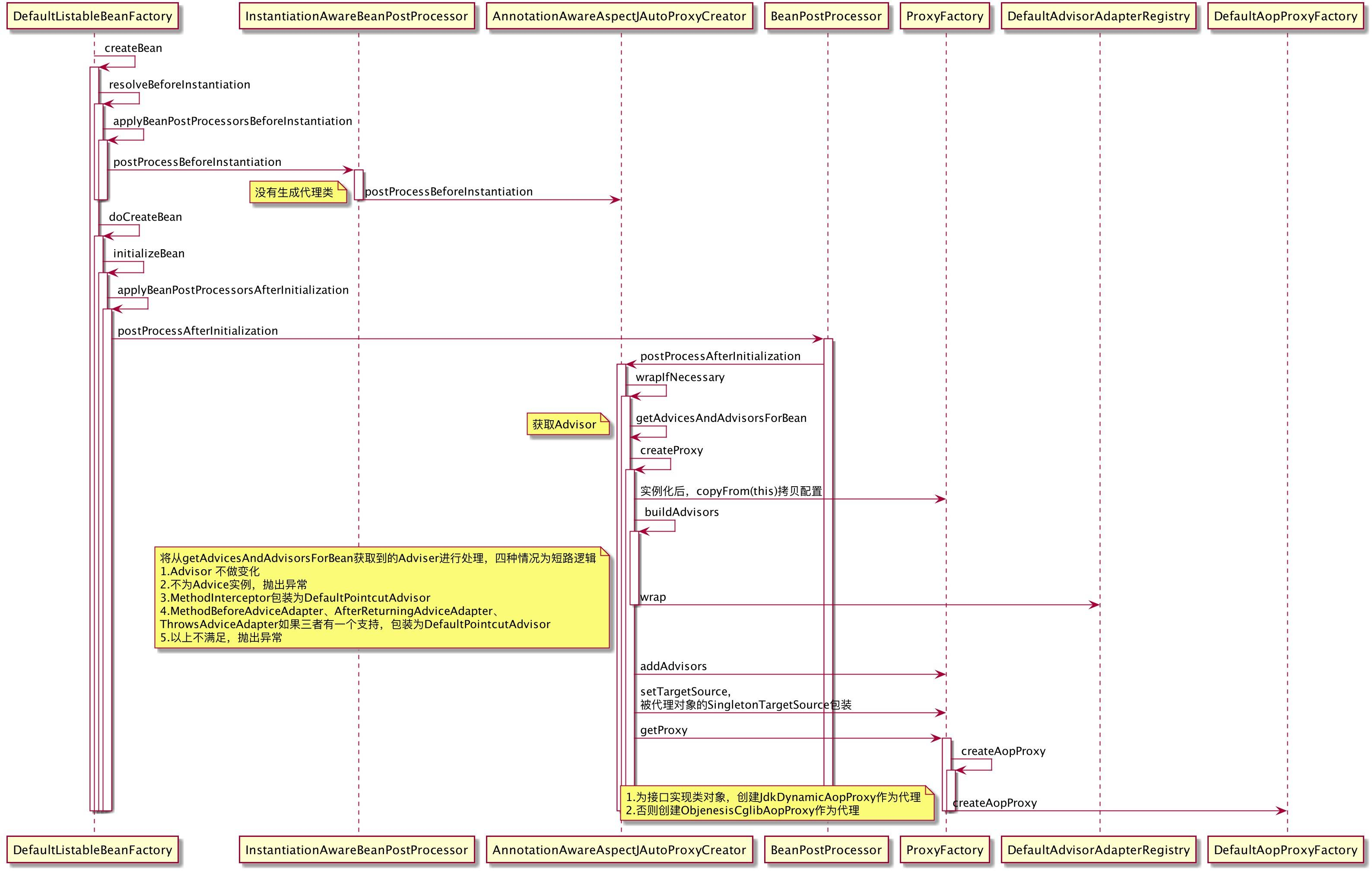
创建代理流程
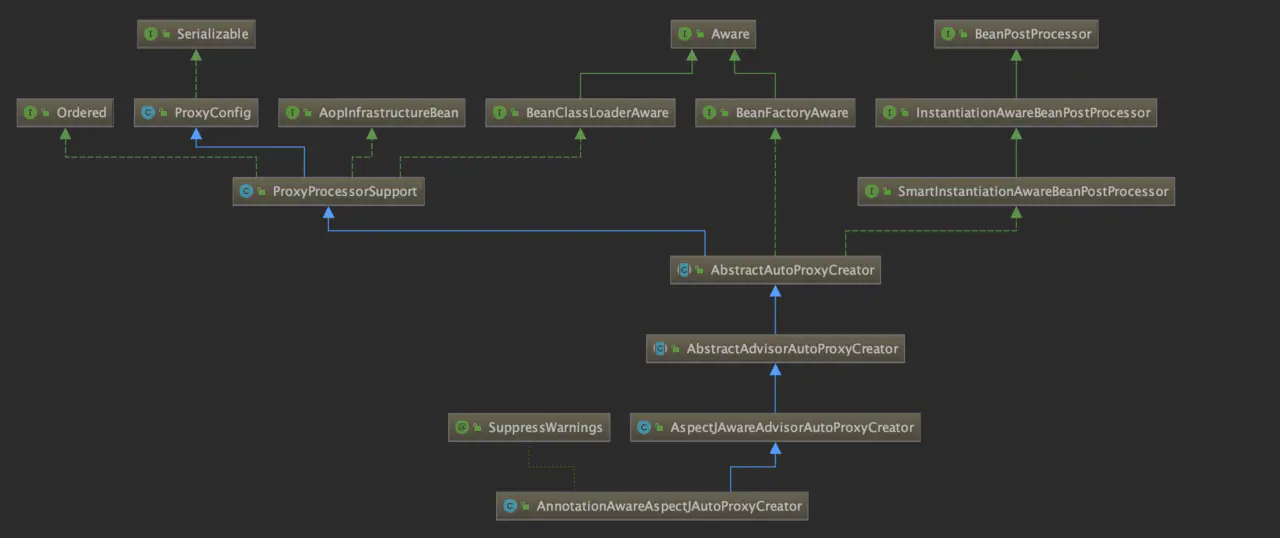
AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator结构
由@EnableAspectJAutoProxy导入的AspectJAutoProxyRegistrar注册到beanfactory中,作为一个BeanPostProcessor存在
创建代理时序图
调用代理
在了解调用代理的逻辑之前,我们来回顾创建代理对象的方法实现
1 | // JdkDynamicAopProxy.getProxy |
代理类执行代码
1 |
|
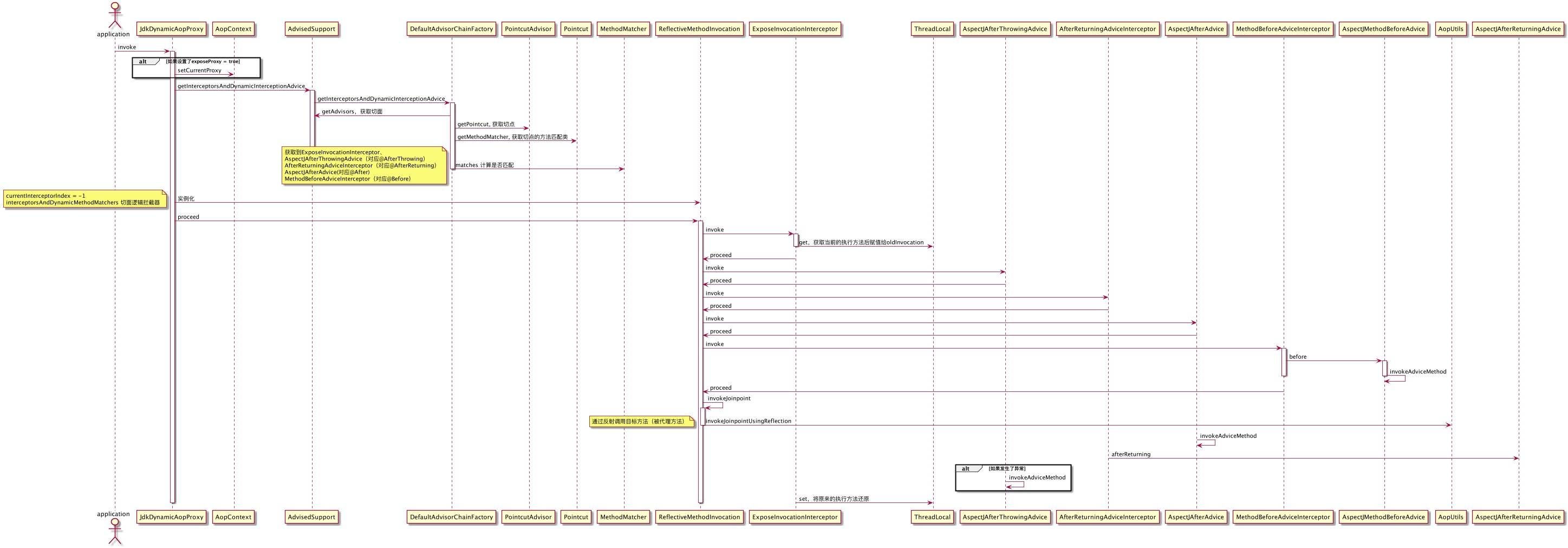
执行时序